Rare dog breeds are notable for their unique physical characteristics, distinct behaviours, and specialised healthcare needs.
Proper care will enable them to be healthy and happy and sustain their uniqueness using the right veterinary products.
This guide provides detailed information about the general veterinary care necessary for rare dog breeds and offers practical recommendations for using proper veterinary products for veterinarians.
Understanding Rare Dog Breeds and Their Unique Needs
Certain varieties are limited in availability due to either low population numbers, their specific origins from certain regions, or the practice of selective breeding.
Some of them include;
- Norwegian Lundehund
- Thai Ridgeback
- Azawakh
They are less likely to be expected, thus resulting in a lower general awareness of their diseases. Therefore, the necessity of veterinary services is even more critical.
Common Challenges in Treating Rare Dog Breeds
- Limited Genetic Diversity
- Rare breeds often come from small gene pools, making them prone to genetic disorders such as:
- Hip dysplasia
- Heart diseases
- Neurological issues
- Rare breeds often come from small gene pools, making them prone to genetic disorders such as:
- Breed-Specific Health Conditions
- Certain breeds have unique physical or physiological traits.
For example:
- Norwegian Lundehund: Prone to gastrointestinal issues like protein-losing enteropathy.
- Shar Pei: Often affected by Shar Pei fever and skin conditions.
- Lack of Established Veterinary Protocols
- Some are rare breeds, so there are no set rules for diagnosing and treating common diseases because vets have to turn to existing literature, medical research, or word-of-mouth.
- Dietary and Environmental Sensitivities
- Some types require specific diets, and certain breeds may be susceptible to certain conditions, like:
- Heat
- Chemical-laden substances
- Some types require specific diets, and certain breeds may be susceptible to certain conditions, like:
Key Veterinary Care Practices for Rare Dog Breeds
- Detailed Medical Histories and Genetic Screening
- Veterinarians should prioritise gathering thorough medical histories and conducting genetic screenings for rare breeds.
- This helps identify potential health risks early and allows for tailored preventive care plans.
| Expert Tip: Collaborate with breed-specific organisations to access genetic databases and updated research. |
- Customised Vaccination and Treatment Plans
- Due to their genetic makeup, rare breeds may respond differently to vaccinations or medications.
- Customised treatment plans can prevent adverse reactions or complications.
Actionable Steps:
- Use titer testing to determine immunity levels before vaccinating.
- Regularly review the breed-specific medical literature.
- Specialised Nutritional Requirements
- Rare dog breeds often require tailored diets to prevent health issues.
For example:
- Azawakh:
- A lean breed that needs high-protein, low-fat diets to maintain their athletic build.
- Dandie Dinmont Terrier:
- Prone to obesity, requiring portion-controlled feeding.
Nutritional Chart for Rare Dog Breeds
The chart below provides dietary guidelines based on breed size and activity level:
| Breed | Diet Type | Key Nutrients | Feeding Frequency |
| Norwegian Lundehund | Easily digestible diet | Omega-3, probiotics | 2-3 times daily |
| Azawakh | High-protein, low-fat | Protein, essential amino acids | Twice daily |
| Thai Ridgeback | Balanced commercial food | Calcium, fiber | Twice daily |
- Regular Physical Examinations
- Frequent health checks are critical for rare breeds, as early detection of conditions can significantly improve outcomes.
| Expert TipSchedule biannual exams instead of the annual ones recommended for more common breeds. |
During these exams:
- Assess for breed-specific health risks.
- Monitor weight, coat condition, and dental health closely.
- Managing Behavioural and Socialisation Needs
- Rare breeds may display unique behavioural traits requiring early socialisation and training.
For example:
- Xoloitzcuintli: Known for their loyalty but need early socialisation to avoid anxiety.
- Karelian Bear Dog: Requires consistent training to manage their hunting instincts.
| Veterinary Role Recommend certified trainers familiar with rare breeds and provide resources for mental stimulation activities. |
- Preventive Care for Aging Rare Breeds
- As rare breeds age, they may be more susceptible to conditions like:
- Arthritis
- Vision loss
- Organ failure
Preventive Measures Include:
- Joint supplements for breeds prone to arthritis.
- Regular eye examinations are performed for breeds like the Tibetan Mastiff, prone to cataracts.
- Kidney function tests for breeds like the Basenji predisposed to Fanconi syndrome.
- Emergency Preparedness for Rare Breed Conditions
- Rare breeds may require emergency interventions for sudden illnesses. Veterinary clinics should maintain breed-specific emergency care guides.
| Example: A veterinarian treating a Shar Pei must be prepared to manage sudden fevers or swollen joints due to Shar Pei fever. |
The Role of Technology in Rare Breed Veterinary Care
With technological advancements, veterinarians can improve diagnostics and treatment for rare breeds.
- Telemedicine:
- Consult with specialists worldwide for breed-specific advice.
- Wearable Tech:
- Health monitoring devices track activity levels and detect abnormalities in real time.
Addressing Common Concerns for Rare Dog Breeds
Environmental Adaptations
Some rare breeds are susceptible to environmental changes. Ensure they are kept in conditions suitable for their breed origins.
- Cold-weather breeds (e.g., Karelian Bear Dog): Require insulated shelters.
- Desert breeds (e.g., Azawakh): Need protection from cold and wet conditions.
Accessing Veterinary Products and Supplies
The animals belonging to rare breeds may require specific veterinary products, including:
- Drugs
- Food supplements
- And grooming tools
The site’s need fulfillment feature allows veterinary surgeons and pet owners to browse the range of veterinary supplies in search of individual requirements.
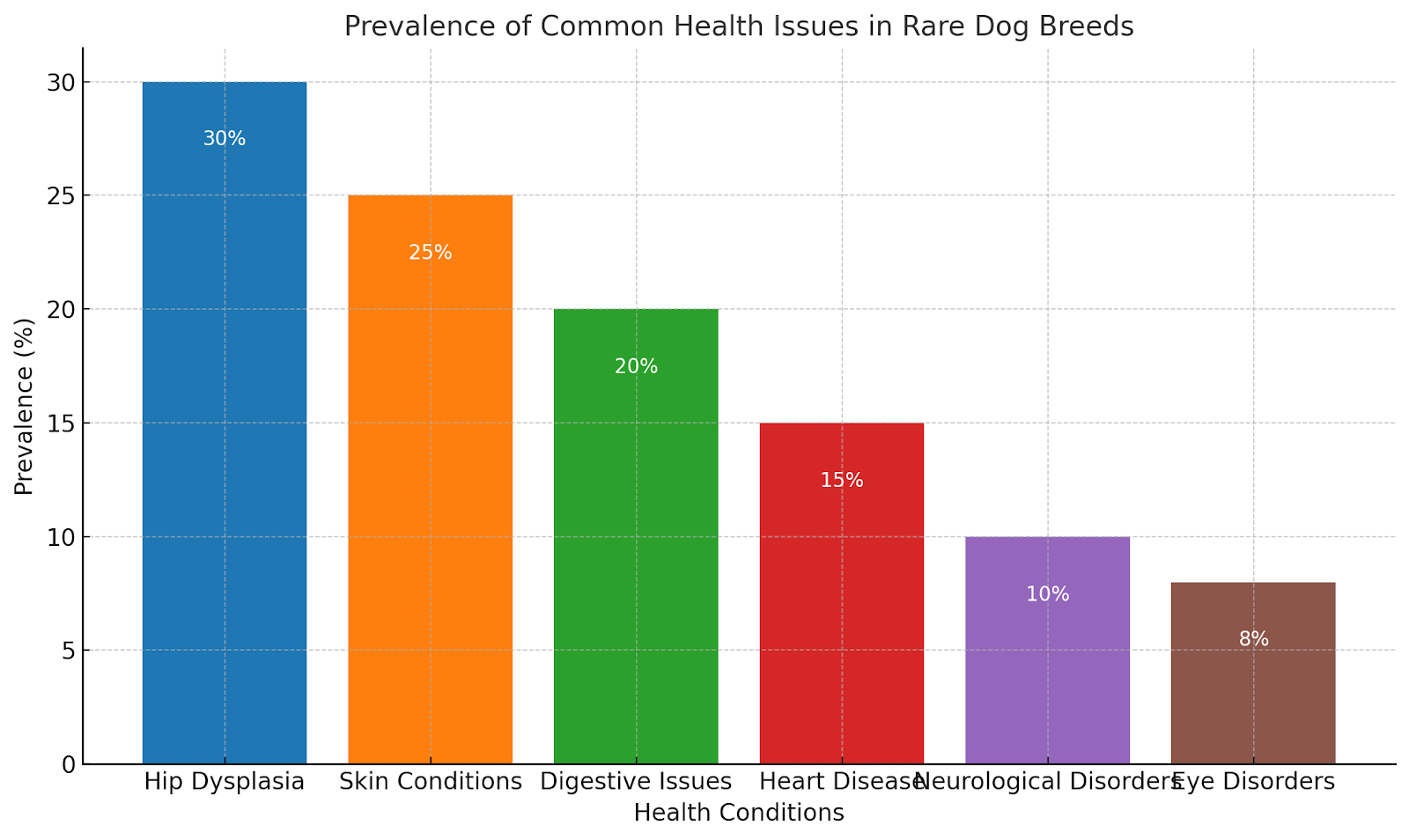
Graph: Common Health Issues in Rare Dog Breeds
The following graph highlights the prevalence of common health conditions in rare breeds:

Conclusion
Certain dog breeds have unique needs and should be cared for with specialised formulations that address their genetic traits, dietary requirements, and environmental conditions.
Veterinarians should be familiar with breed specialisation, as it is essential for breed health and successful collaborations with breed associations.
This is all about how you can prevent most of these diseases in your extraordinary dogs and how to address them since each dog is unique.
DVM Central is a reliable marketplace for all types of animal care products. It directly connects suppliers and buyers to streamline the buying and selling process for veterinary supplies.
At this marketplace, veterinarians can register for virtual expos to stay updated on the latest advancements in the veterinary field. Moreover, you can earn free CE credits.
FAQs
How can I find the right veterinary supplies for a rare dog breed?
You can search online shops that supply particular veterinary goods and services according to your breed. You need to seek advice from your veterinarian.
Are rare dog breeds harder to train?
It depends on the breed. Some, for instance, the Xoloitzcuintli dog breed, are easy to train in social communication once socialised, but others, like the Karelian Bear Dog breed, may be hard to train due to their strong herding instincts.
What should I feed a rare dog breed with dietary sensitivities?
You should feed them the food that corresponds to their breed specialty, either based on their size, activity level, or any health concerns they might have. Therefore, you should consult with your veterinarian on how to develop an appropriate meal plan.